Emerging Workforce – Changing Needs
Print this Article | Send to Colleague
Emerging Workforce ? Changing Needs
Why do we continue to have OHS incidents? Statistics continue to prove that we are not resolving this issue positively, bearing in mind there are no accidents. Having completed an analysis of what our (high school student) emerging workforce is being offered regarding Occupational Health and Safety; we continually fall short of the mark.
Of 150,000 online courses taken by high school students in Western Canada through SafetyinSchools.ca, the top three OHS courses assigned to students by their teachers are:
- hazard awareness
- hazard recognition, and
- job safety analysis
These are critical elements of OHS that must be an integral part of our youths'' development before they become a statistical lagging indicator.
Until recently, mental health has not been part of the workplace hazard risk equation. Managing risk has been concentrated on identifying physical hazards and mitigating them with engineering, administrative, and personal protective equipment controls.
A direct result of examining the life-changing injuries sustained at work by young, less experienced youth resulted in the recognition that mental health and suitability for work based on an individual's own state of mental health, peer pressures and the desire to "get 'er done" are critical elements of their Risk Factor.
One study found that a staggering 90% of all workplace injuries are due to the worker's state of mind not the physical hazard. Another study found that 82% of employees with mental health issues admit it impacts their work while only 53% of those with physical health issues say that it impacts their work.
Taking advantage of technology and understanding that our new workers have embraced hand-held devices that are now essential to their daily lives, we must exploit this way to influence their behaviour and bring this into their consciousness at work.
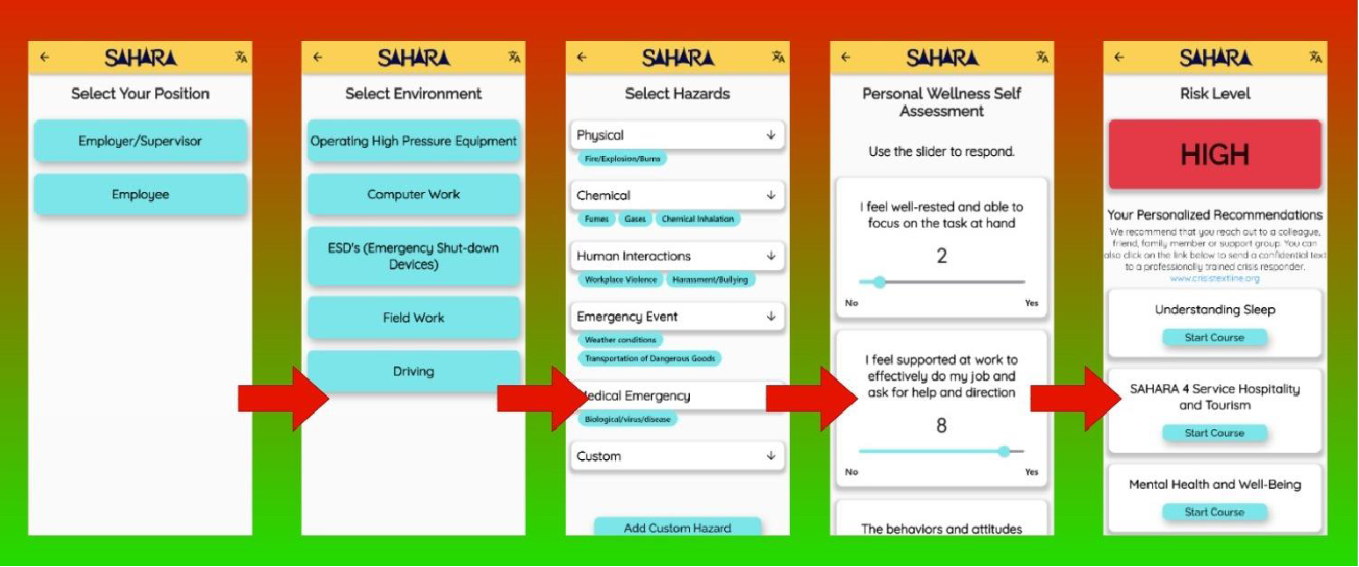
A most exciting online tool is the Safety and Hazard Awareness Risk Assessment (SAHARA), which combines the worker's confidential, personal wellness self-assessment with the workplace hazards they identify to calculate their own personal risk level.
Let's examine factors that must be included independent of the workplace and duties e.g., mental fitness-for-work, alertness, sleep, distraction, alcohol or drug-impairment components, dehydration, stress, fatigue, shiftwork, anxiety in personal life, despair.
Other hazards relate to how the worker is engaged and tasked in the workplace, but which the worker does not want to disclose. These may include confidence, self-assessed ability, training, accident history, peer pressure, asking for help, pressure to complete work, support, etc.
Delivered in over 100 languages from any device, this mobile device-enabled software assists the young worker with identification of potential hazards and the impact on their mental health in the workplace, based on their current own state of mind and present mental health. Hazard risk matrices can be customized for regional HSE regulations, workplace settings and practices, or even corporate office settings.
Both supervisors and young workers can complete the hazard assessment for comparison reporting and continuous safety performance improvement opportunities. Any hazard not listed can be added promoting a proactive culture, accurate real-time hazard assessments, and comprehensive reporting of overall workplace risk and mitigation.
Training recommendations are generated that include eLearning and/or links to other training and critical resources. Workers that indicate feelings of despair trigger a High-Risk level and a direct link to an anonymous crisis response support organization or as directed by the company.
Individually focused training recommendations are generated that include eLearning and/or links to other training and critical resources. Workers that indicate feelings of despair trigger a High-Risk level and a direct link to an anonymous crisis response support organization or as required by the employer.
We must combine current technology with dynamic input by the user. This will reinforce how and where their risks can be reduced, providing them with success when they embrace it.
SAHARA was developed by SWIFT Learning a social enterprise company and co-founder of the SiS Foundation of Canada. SWIFT and SiS are dedicated to delivering solutions that educate and empower youth to stay safe at work, school, home and at play 4 Life. SAHARA is delivered free to Canadian High Schools.
Utility Safety Partners Education and Awareness Committee

