UPS Fueling Mississippi Fleet With RNG
 UPS is making strides to power its Jackson, MS fleet with renewable natural gas (RNG). According to Susan Rosenberg, UPS Public Relations Director, the renewable natural gas will come from landfill waste.
UPS is making strides to power its Jackson, MS fleet with renewable natural gas (RNG). According to Susan Rosenberg, UPS Public Relations Director, the renewable natural gas will come from landfill waste.
Currently, UPS is using liquified natural gas to fuel its large tractor-trailers, Rosenberg said. "We have a variety of natural gas — compressed, liquified, propane — and now we’re expanding, looking at renewable," she said.
To ramp up its efforts, in 2014 UPS built a natural gas fueling station for liquified natural gas in Jackson, MS. There's also a fueling station in Memphis so trucks can go from "hub to hub," Rosenberg said. "Jackson is an important UPS location that is part of what we call a rolling laboratory for testing various equipment and fuel."
"Our UPS alternative fuel and advanced technology fleet includes more than 6,430 all-electric, hybrid electric, natural gas, renewable fuels, biomethane, and light-weight fuel-saving composite body vehicles," Rosenberg said. "Our rolling laboratory approach provides the real-world bridge between research and commercialization and allows UPS to scale up the right solutions for the driving and delivery circumstances. This will conserve fuel, reduce emissions, and sustain UPS operating efficiency and service."
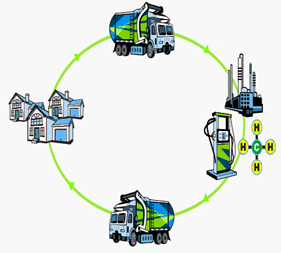
The RNG will fuel more than 140 heavy duty trucks in Memphis and Jackson, part of UPS’s natural gas fleet, which includes more than 3,800 medium and heavy duty vehicles worldwide. RNG, also known as biomethane, can be derived from many abundant and renewable sources, including decomposing organic waste in landfills, wastewater treatment, and agriculture. It is then distributed through the natural gas pipeline system, making it available for use as liquefied natural gas (LNG) or compressed natural gas (CNG).
In 2014, 5.4 percent of total gas and diesel purchased by UPS was displaced by using alternative fuels. UPS has a goal to reach a billion miles traveled by this advanced fleet by 2017.
 UPS is making strides to power its Jackson, MS fleet with renewable natural gas (RNG). According to Susan Rosenberg, UPS Public Relations Director, the renewable natural gas will come from landfill waste.
UPS is making strides to power its Jackson, MS fleet with renewable natural gas (RNG). According to Susan Rosenberg, UPS Public Relations Director, the renewable natural gas will come from landfill waste.