Rengo Developing New Cellulose Nanofiber Using Cellophane Production Technology
![]() Print this Article | Send to Colleague
Print this Article | Send to Colleague
Rengo Co. (Osaka, Japan) announced this past month that it has applied cellulose production technology to develop Xanthated Cellulose Nanofiber (XCNF®), a new cellulose nanofiber.
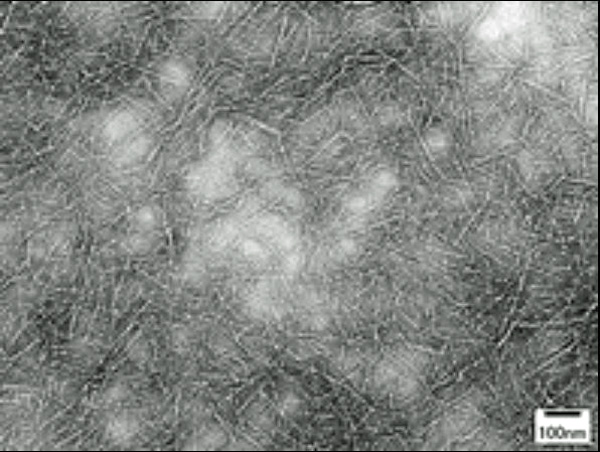
Pictured above: The visual structure of XCNF (viewed through a transmission electron microscope).
Cellulose nanofiber is a fibrous substance made by microfiberizing cellulose in wood cellulose fiber to the nanometer level* using chemical or mechanical processes. It is said to have one fifth the weight of steel but five times its strength. Cellulose nanofiber has drawn a great deal of attention in recent years as a next-generation material that can be applied to various purposes, such as reducing the weight of automobiles. (* 1 nm = 0.000001 mm = 10-9 m)
Rengo focused on the production technology of cellophane manufactured at its Takefu Plant, independently developing a technology using the intermediate product, cellulose xanthate, to produce cellulose nanofiber. XCNF has xanthate groups in its cellulose molecules, but it is possible to remove these groups with simple processing to convert XCNF into cellulose nanofiber such as that made from pure cellulose.
Rengo made a presentation regarding the development of XCNF at the 85th Pulp and Paper Research Conference (organized by the Japan Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry) held on June 20, 2018. Moving forward, Rengo will collaborate with companies and universities on fundamental research and merchandise development utilizing the features of XCNF so as to work toward its practical application.


